Dynamic Dataset(s) Accessing
How to Create a file for multiple datafiles execution
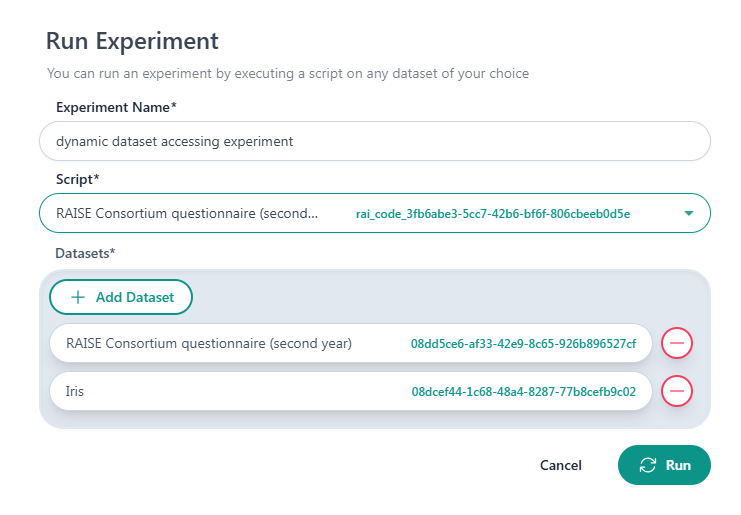
The order datasets are added when a new experiment is created, corresponds to the order of the datasets in the list dataset_ids, which is stored in the RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST environment variable. Therefore, in the following case of a new experiment the first dataset is the “RAISE Consortium questionnaire (second…)” and the second dataset is the “Iris”.
The id of the first dataset is in the first element of the dataset_ids list, the second dataset id is stored in the second element, and so on. Make sure the dataset UUIDs are loaded in your script in the correct order to avoid errors or inconsistencies during the execution. This loading method allows you to use multiple datasets (of any type) within a single script (dynamic dataset accessing). In the remaining sections, we provide some examples to access the aforementioned list with different programming languages.
The process of mapping the selected dataset ids into the experiment environment is automatically orchestrated in the portal.
However, when debugging an experiment locally, you must manually specify which datafiles will be used. In order to do this, create a .env file in the root directory of the experiment. This file must contain a variable named RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST with a list of the dataset ids. This allows you to access the dataset identifiers within the experiment’s main script and load the corresponding datafiles correctly.
RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST=["00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001","00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000002"]To apply the same scripts in another experiment with same files types, you have to create the experiment having as first dataset in the experiment a dataset similar to the “RAISE Consortium questionnaire (second…)” and another one similar to the “Iris” dataset. This way the script will read the corresponding datasets dynamically.
Python
To read them in python, you have to import json, and follow the next example:
import jsonfrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()dataset_ids = json.loads(os.getenv("RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST"))xls = pd.ExcelFile(f"{dataset_ids[0]}/datafile.xlsx", engine = 'openpyxl')NodeJS
To read them in NodeJs:
import dotenv from 'dotenv';dotenv.config(); // safe to call even if .env (local environment variables) doesn't exist
const datasetIds = JSON.parse(process.env.RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST || "[]");
if (!Array.isArray(datasetIds) || datasetIds.length === 0) { console.error("RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST is missing or empty."); process.exit(1);}
const csvFilePath = `${datasetIds[0]}/datafile.csv`;R
To read them in R:
library(dotenv)library(jsonlite)
# --- Load environment locally ---if (file.exists(".env")) load_dot_env(file = ".env")
# --- Load dataset ID list ---dataset_env <- Sys.getenv("RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST")if (dataset_env == "") { stop("Environment variable RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST is missing.")}
dataset_ids <- fromJSON(dataset_env)if (length(dataset_ids) == 0) { stop("RAISE_DATASET_ID_LIST is empty or invalid JSON.")}
# Access the filecsv_file_path <- file.path(dataset_ids[[1]], "datafile.csv")For further details, please refer to section https://documentation.raise-science.eu/how-to/write-script/python/